| 1 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 2 |
|
- |
|
* LibXDiff by Davide Libenzi ( File Differential Library )
|
| 3 |
|
- |
|
* Copyright (C) 2003-2016 Davide Libenzi, Johannes E. Schindelin
|
| 4 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 5 |
|
- |
|
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
| 6 |
|
- |
|
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
| 7 |
|
- |
|
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
|
| 8 |
|
- |
|
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
| 9 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 10 |
|
- |
|
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
| 11 |
|
- |
|
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
| 12 |
|
- |
|
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
|
| 13 |
|
- |
|
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
|
| 14 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 15 |
|
- |
|
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
|
| 16 |
|
- |
|
* License along with this library; if not, see
|
| 17 |
|
- |
|
* <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
| 18 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 19 |
|
- |
|
* Davide Libenzi <davidel@xmailserver.org>
|
| 20 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 21 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 22 |
|
- |
|
#include "xinclude.h"
|
| 23 |
|
- |
|
#include "xtypes.h"
|
| 24 |
|
- |
|
#include "xdiff.h"
|
| 25 |
|
- |
|
|
| 26 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 27 |
|
- |
|
* The basic idea of patience diff is to find lines that are unique in
|
| 28 |
|
- |
|
* both files. These are intuitively the ones that we want to see as
|
| 29 |
|
- |
|
* common lines.
|
| 30 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 31 |
|
- |
|
* The maximal ordered sequence of such line pairs (where ordered means
|
| 32 |
|
- |
|
* that the order in the sequence agrees with the order of the lines in
|
| 33 |
|
- |
|
* both files) naturally defines an initial set of common lines.
|
| 34 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 35 |
|
- |
|
* Now, the algorithm tries to extend the set of common lines by growing
|
| 36 |
|
- |
|
* the line ranges where the files have identical lines.
|
| 37 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 38 |
|
- |
|
* Between those common lines, the patience diff algorithm is applied
|
| 39 |
|
- |
|
* recursively, until no unique line pairs can be found; these line ranges
|
| 40 |
|
- |
|
* are handled by the well-known Myers algorithm.
|
| 41 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 42 |
|
- |
|
|
| 43 |
|
- |
|
#define NON_UNIQUE ULONG_MAX
|
| 44 |
|
- |
|
|
| 45 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 46 |
|
- |
|
* This is a hash mapping from line hash to line numbers in the first and
|
| 47 |
|
- |
|
* second file.
|
| 48 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 49 |
|
- |
|
struct hashmap {
|
| 50 |
|
- |
|
int nr, alloc;
|
| 51 |
|
- |
|
struct entry {
|
| 52 |
|
- |
|
unsigned long hash;
|
| 53 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 54 |
|
- |
|
* 0 = unused entry, 1 = first line, 2 = second, etc.
|
| 55 |
|
- |
|
* line2 is NON_UNIQUE if the line is not unique
|
| 56 |
|
- |
|
* in either the first or the second file.
|
| 57 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 58 |
|
- |
|
unsigned long line1, line2;
|
| 59 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 60 |
|
- |
|
* "next" & "previous" are used for the longest common
|
| 61 |
|
- |
|
* sequence;
|
| 62 |
|
- |
|
* initially, "next" reflects only the order in file1.
|
| 63 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 64 |
|
- |
|
struct entry *next, *previous;
|
| 65 |
|
- |
|
|
| 66 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 67 |
|
- |
|
* If 1, this entry can serve as an anchor. See
|
| 68 |
|
- |
|
* Documentation/diff-options.txt for more information.
|
| 69 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 70 |
|
- |
|
unsigned anchor : 1;
|
| 71 |
|
- |
|
} *entries, *first, *last;
|
| 72 |
|
- |
|
/* were common records found? */
|
| 73 |
|
- |
|
unsigned long has_matches;
|
| 74 |
|
- |
|
mmfile_t *file1, *file2;
|
| 75 |
|
- |
|
xdfenv_t *env;
|
| 76 |
|
- |
|
xpparam_t const *xpp;
|
| 77 |
|
- |
|
};
|
| 78 |
|
- |
|
|
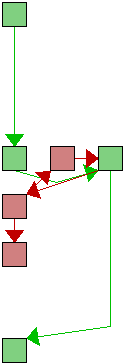
| 79 |
 |
6 |
2 |
static int is_anchor(xpparam_t const *xpp, const char *line)
|
| 80 |
- |
|
{
|
| 81 |
- |
|
unsigned long i;
|
| 82 |
6 |
2,5,6 |
for (i = 0; i < xpp->anchors_nr; i++) {
|
| 83 |
##### |
3 |
if (!strncmp(line, xpp->anchors[i], strlen(xpp->anchors[i])))
|
| 84 |
##### |
4 |
return 1;
|
| 85 |
- |
|
}
|
| 86 |
6 |
7 |
return 0;
|
| 87 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 88 |
|
- |
|
|
| 89 |
|
- |
|
/* The argument "pass" is 1 for the first file, 2 for the second. */
|
| 90 |
 |
17 |
2 |
static void insert_record(xpparam_t const *xpp, int line, struct hashmap *map,
|
| 91 |
- |
|
int pass)
|
| 92 |
- |
|
{
|
| 93 |
17 |
5 |
xrecord_t **records = pass == 1 ?
|
| 94 |
17 |
2-4 |
map->env->xdf1.recs : map->env->xdf2.recs;
|
| 95 |
17 |
5 |
xrecord_t *record = records[line - 1], *other;
|
| 96 |
- |
|
/*
|
| 97 |
- |
|
* After xdl_prepare_env() (or more precisely, due to
|
| 98 |
- |
|
* xdl_classify_record()), the "ha" member of the records (AKA lines)
|
| 99 |
- |
|
* is _not_ the hash anymore, but a linearized version of it. In
|
| 100 |
- |
|
* other words, the "ha" member is guaranteed to start with 0 and
|
| 101 |
- |
|
* the second record's ha can only be 0 or 1, etc.
|
| 102 |
- |
|
*
|
| 103 |
- |
|
* So we multiply ha by 2 in the hope that the hashing was
|
| 104 |
- |
|
* "unique enough".
|
| 105 |
- |
|
*/
|
| 106 |
17 |
5 |
int index = (int)((record->ha << 1) % map->alloc);
|
| 107 |
- |
|
|
| 108 |
17 |
5,19 |
while (map->entries[index].line1) {
|
| 109 |
11 |
6 |
other = map->env->xdf1.recs[map->entries[index].line1 - 1];
|
| 110 |
11 |
6,8 |
if (map->entries[index].hash != record->ha ||
|
| 111 |
11 |
7 |
!xdl_recmatch(record->ptr, record->size,
|
| 112 |
- |
|
other->ptr, other->size,
|
| 113 |
11 |
7 |
map->xpp->flags)) {
|
| 114 |
##### |
9 |
if (++index >= map->alloc)
|
| 115 |
##### |
10 |
index = 0;
|
| 116 |
##### |
11 |
continue;
|
| 117 |
- |
|
}
|
| 118 |
11 |
12 |
if (pass == 2)
|
| 119 |
7 |
13 |
map->has_matches = 1;
|
| 120 |
11 |
14,15 |
if (pass == 1 || map->entries[index].line2)
|
| 121 |
7 |
16 |
map->entries[index].line2 = NON_UNIQUE;
|
| 122 |
- |
|
else
|
| 123 |
4 |
17 |
map->entries[index].line2 = line;
|
| 124 |
11 |
18 |
return;
|
| 125 |
- |
|
}
|
| 126 |
6 |
20 |
if (pass == 2)
|
| 127 |
##### |
21 |
return;
|
| 128 |
6 |
22 |
map->entries[index].line1 = line;
|
| 129 |
6 |
22 |
map->entries[index].hash = record->ha;
|
| 130 |
6 |
22 |
map->entries[index].anchor = is_anchor(xpp, map->env->xdf1.recs[line - 1]->ptr);
|
| 131 |
6 |
23 |
if (!map->first)
|
| 132 |
1 |
24 |
map->first = map->entries + index;
|
| 133 |
6 |
25 |
if (map->last) {
|
| 134 |
5 |
26 |
map->last->next = map->entries + index;
|
| 135 |
5 |
26 |
map->entries[index].previous = map->last;
|
| 136 |
- |
|
}
|
| 137 |
6 |
27 |
map->last = map->entries + index;
|
| 138 |
6 |
27 |
map->nr++;
|
| 139 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 140 |
|
- |
|
|
| 141 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 142 |
|
- |
|
* This function has to be called for each recursion into the inter-hunk
|
| 143 |
|
- |
|
* parts, as previously non-unique lines can become unique when being
|
| 144 |
|
- |
|
* restricted to a smaller part of the files.
|
| 145 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 146 |
|
- |
|
* It is assumed that env has been prepared using xdl_prepare().
|
| 147 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 148 |
 |
1 |
2 |
static int fill_hashmap(mmfile_t *file1, mmfile_t *file2,
|
| 149 |
- |
|
xpparam_t const *xpp, xdfenv_t *env,
|
| 150 |
- |
|
struct hashmap *result,
|
| 151 |
- |
|
int line1, int count1, int line2, int count2)
|
| 152 |
- |
|
{
|
| 153 |
1 |
2 |
result->file1 = file1;
|
| 154 |
1 |
2 |
result->file2 = file2;
|
| 155 |
1 |
2 |
result->xpp = xpp;
|
| 156 |
1 |
2 |
result->env = env;
|
| 157 |
- |
|
|
| 158 |
- |
|
/* We know exactly how large we want the hash map */
|
| 159 |
1 |
2 |
result->alloc = count1 * 2;
|
| 160 |
1 |
3 |
result->entries = (struct entry *)
|
| 161 |
1 |
2 |
xdl_malloc(result->alloc * sizeof(struct entry));
|
| 162 |
1 |
3 |
if (!result->entries)
|
| 163 |
##### |
4 |
return -1;
|
| 164 |
1 |
5 |
memset(result->entries, 0, result->alloc * sizeof(struct entry));
|
| 165 |
- |
|
|
| 166 |
- |
|
/* First, fill with entries from the first file */
|
| 167 |
11 |
5,7 |
while (count1--)
|
| 168 |
10 |
6 |
insert_record(xpp, line1++, result, 1);
|
| 169 |
- |
|
|
| 170 |
- |
|
/* Then search for matches in the second file */
|
| 171 |
8 |
8,10 |
while (count2--)
|
| 172 |
7 |
9 |
insert_record(xpp, line2++, result, 2);
|
| 173 |
- |
|
|
| 174 |
1 |
11 |
return 0;
|
| 175 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 176 |
|
- |
|
|
| 177 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 178 |
|
- |
|
* Find the longest sequence with a smaller last element (meaning a smaller
|
| 179 |
|
- |
|
* line2, as we construct the sequence with entries ordered by line1).
|
| 180 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 181 |
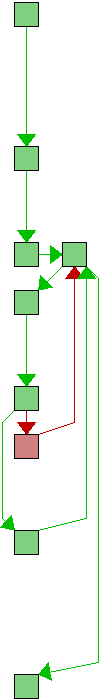 |
4 |
2 |
static int binary_search(struct entry **sequence, int longest,
|
| 182 |
- |
|
struct entry *entry)
|
| 183 |
- |
|
{
|
| 184 |
4 |
2 |
int left = -1, right = longest;
|
| 185 |
- |
|
|
| 186 |
9 |
2,6 |
while (left + 1 < right) {
|
| 187 |
5 |
3 |
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
|
| 188 |
- |
|
/* by construction, no two entries can be equal */
|
| 189 |
5 |
3 |
if (sequence[middle]->line2 > entry->line2)
|
| 190 |
##### |
4 |
right = middle;
|
| 191 |
- |
|
else
|
| 192 |
5 |
5 |
left = middle;
|
| 193 |
- |
|
}
|
| 194 |
- |
|
/* return the index in "sequence", _not_ the sequence length */
|
| 195 |
4 |
7 |
return left;
|
| 196 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 197 |
|
- |
|
|
| 198 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 199 |
|
- |
|
* The idea is to start with the list of common unique lines sorted by
|
| 200 |
|
- |
|
* the order in file1. For each of these pairs, the longest (partial)
|
| 201 |
|
- |
|
* sequence whose last element's line2 is smaller is determined.
|
| 202 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 203 |
|
- |
|
* For efficiency, the sequences are kept in a list containing exactly one
|
| 204 |
|
- |
|
* item per sequence length: the sequence with the smallest last
|
| 205 |
|
- |
|
* element (in terms of line2).
|
| 206 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 207 |
 |
1 |
2 |
static struct entry *find_longest_common_sequence(struct hashmap *map)
|
| 208 |
- |
|
{
|
| 209 |
1 |
2 |
struct entry **sequence = xdl_malloc(map->nr * sizeof(struct entry *));
|
| 210 |
1 |
3 |
int longest = 0, i;
|
| 211 |
- |
|
struct entry *entry;
|
| 212 |
- |
|
|
| 213 |
- |
|
/*
|
| 214 |
- |
|
* If not -1, this entry in sequence must never be overridden.
|
| 215 |
- |
|
* Therefore, overriding entries before this has no effect, so
|
| 216 |
- |
|
* do not do that either.
|
| 217 |
- |
|
*/
|
| 218 |
1 |
3 |
int anchor_i = -1;
|
| 219 |
- |
|
|
| 220 |
1 |
3 |
if (!sequence)
|
| 221 |
##### |
4 |
return NULL;
|
| 222 |
- |
|
|
| 223 |
7 |
5,19,20 |
for (entry = map->first; entry; entry = entry->next) {
|
| 224 |
6 |
6,7 |
if (!entry->line2 || entry->line2 == NON_UNIQUE)
|
| 225 |
2 |
8 |
continue;
|
| 226 |
4 |
9 |
i = binary_search(sequence, longest, entry);
|
| 227 |
4 |
10-12 |
entry->previous = i < 0 ? NULL : sequence[i];
|
| 228 |
4 |
13 |
++i;
|
| 229 |
4 |
13 |
if (i <= anchor_i)
|
| 230 |
##### |
14 |
continue;
|
| 231 |
4 |
15 |
sequence[i] = entry;
|
| 232 |
4 |
15 |
if (entry->anchor) {
|
| 233 |
##### |
16 |
anchor_i = i;
|
| 234 |
##### |
16 |
longest = anchor_i + 1;
|
| 235 |
4 |
17 |
} else if (i == longest) {
|
| 236 |
4 |
18 |
longest++;
|
| 237 |
- |
|
}
|
| 238 |
- |
|
}
|
| 239 |
- |
|
|
| 240 |
- |
|
/* No common unique lines were found */
|
| 241 |
1 |
21 |
if (!longest) {
|
| 242 |
##### |
22 |
xdl_free(sequence);
|
| 243 |
##### |
23 |
return NULL;
|
| 244 |
- |
|
}
|
| 245 |
- |
|
|
| 246 |
- |
|
/* Iterate starting at the last element, adjusting the "next" members */
|
| 247 |
1 |
24 |
entry = sequence[longest - 1];
|
| 248 |
1 |
24 |
entry->next = NULL;
|
| 249 |
4 |
24,26 |
while (entry->previous) {
|
| 250 |
3 |
25 |
entry->previous->next = entry;
|
| 251 |
3 |
25 |
entry = entry->previous;
|
| 252 |
- |
|
}
|
| 253 |
1 |
27 |
xdl_free(sequence);
|
| 254 |
1 |
28 |
return entry;
|
| 255 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 256 |
|
- |
|
|
| 257 |
 |
2 |
2 |
static int match(struct hashmap *map, int line1, int line2)
|
| 258 |
- |
|
{
|
| 259 |
2 |
2 |
xrecord_t *record1 = map->env->xdf1.recs[line1 - 1];
|
| 260 |
2 |
2 |
xrecord_t *record2 = map->env->xdf2.recs[line2 - 1];
|
| 261 |
2 |
2 |
return xdl_recmatch(record1->ptr, record1->size,
|
| 262 |
|
2 |
2 |
record2->ptr, record2->size, map->xpp->flags);
|
| 263 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 264 |
|
- |
|
|
| 265 |
|
- |
|
static int patience_diff(mmfile_t *file1, mmfile_t *file2,
|
| 266 |
|
- |
|
xpparam_t const *xpp, xdfenv_t *env,
|
| 267 |
|
- |
|
int line1, int count1, int line2, int count2);
|
| 268 |
|
- |
|
|
| 269 |
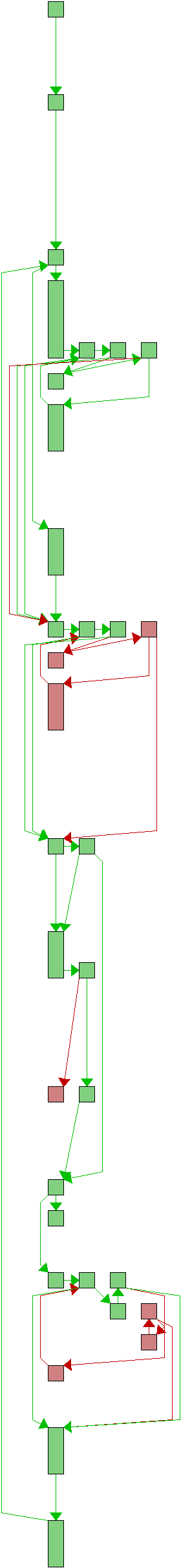 |
1 |
2 |
static int walk_common_sequence(struct hashmap *map, struct entry *first,
|
| 270 |
- |
|
int line1, int count1, int line2, int count2)
|
| 271 |
- |
|
{
|
| 272 |
1 |
2 |
int end1 = line1 + count1, end2 = line2 + count2;
|
| 273 |
- |
|
int next1, next2;
|
| 274 |
- |
|
|
| 275 |
- |
|
for (;;) {
|
| 276 |
- |
|
/* Try to grow the line ranges of common lines */
|
| 277 |
5 |
3 |
if (first) {
|
| 278 |
4 |
4 |
next1 = first->line1;
|
| 279 |
4 |
4 |
next2 = first->line2;
|
| 280 |
6 |
4,6,7,9 |
while (next1 > line1 && next2 > line2 &&
|
| 281 |
2 |
8 |
match(map, next1 - 1, next2 - 1)) {
|
| 282 |
2 |
5 |
next1--;
|
| 283 |
2 |
5 |
next2--;
|
| 284 |
- |
|
}
|
| 285 |
- |
|
} else {
|
| 286 |
1 |
10 |
next1 = end1;
|
| 287 |
1 |
10 |
next2 = end2;
|
| 288 |
- |
|
}
|
| 289 |
5 |
11,13,14,16 |
while (line1 < next1 && line2 < next2 &&
|
| 290 |
##### |
15 |
match(map, line1, line2)) {
|
| 291 |
##### |
12 |
line1++;
|
| 292 |
##### |
12 |
line2++;
|
| 293 |
- |
|
}
|
| 294 |
- |
|
|
| 295 |
- |
|
/* Recurse */
|
| 296 |
5 |
17,18 |
if (next1 > line1 || next2 > line2) {
|
| 297 |
- |
|
struct hashmap submap;
|
| 298 |
- |
|
|
| 299 |
3 |
19 |
memset(&submap, 0, sizeof(submap));
|
| 300 |
3 |
19,20 |
if (patience_diff(map->file1, map->file2,
|
| 301 |
- |
|
map->xpp, map->env,
|
| 302 |
- |
|
line1, next1 - line1,
|
| 303 |
- |
|
line2, next2 - line2))
|
| 304 |
3 |
21,22 |
return -1;
|
| 305 |
- |
|
}
|
| 306 |
- |
|
|
| 307 |
5 |
23 |
if (!first)
|
| 308 |
1 |
24 |
return 0;
|
| 309 |
- |
|
|
| 310 |
4 |
25,27,28 |
while (first->next &&
|
| 311 |
3 |
28,29 |
first->next->line1 == first->line1 + 1 &&
|
| 312 |
##### |
29 |
first->next->line2 == first->line2 + 1)
|
| 313 |
##### |
26 |
first = first->next;
|
| 314 |
- |
|
|
| 315 |
4 |
30 |
line1 = first->line1 + 1;
|
| 316 |
4 |
30 |
line2 = first->line2 + 1;
|
| 317 |
- |
|
|
| 318 |
4 |
30 |
first = first->next;
|
| 319 |
4 |
30 |
}
|
| 320 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 321 |
|
- |
|
|
| 322 |
 |
##### |
2 |
static int fall_back_to_classic_diff(struct hashmap *map,
|
| 323 |
- |
|
int line1, int count1, int line2, int count2)
|
| 324 |
- |
|
{
|
| 325 |
- |
|
xpparam_t xpp;
|
| 326 |
##### |
2 |
xpp.flags = map->xpp->flags & ~XDF_DIFF_ALGORITHM_MASK;
|
| 327 |
- |
|
|
| 328 |
##### |
2 |
return xdl_fall_back_diff(map->env, &xpp,
|
| 329 |
|
- |
|
line1, count1, line2, count2);
|
| 330 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 331 |
|
- |
|
|
| 332 |
|
- |
|
/*
|
| 333 |
|
- |
|
* Recursively find the longest common sequence of unique lines,
|
| 334 |
|
- |
|
* and if none was found, ask xdl_do_diff() to do the job.
|
| 335 |
|
- |
|
*
|
| 336 |
|
- |
|
* This function assumes that env was prepared with xdl_prepare_env().
|
| 337 |
|
- |
|
*/
|
| 338 |
 |
4 |
2 |
static int patience_diff(mmfile_t *file1, mmfile_t *file2,
|
| 339 |
- |
|
xpparam_t const *xpp, xdfenv_t *env,
|
| 340 |
- |
|
int line1, int count1, int line2, int count2)
|
| 341 |
- |
|
{
|
| 342 |
- |
|
struct hashmap map;
|
| 343 |
- |
|
struct entry *first;
|
| 344 |
4 |
2 |
int result = 0;
|
| 345 |
- |
|
|
| 346 |
- |
|
/* trivial case: one side is empty */
|
| 347 |
4 |
2 |
if (!count1) {
|
| 348 |
2 |
3,5 |
while(count2--)
|
| 349 |
1 |
4 |
env->xdf2.rchg[line2++ - 1] = 1;
|
| 350 |
1 |
6 |
return 0;
|
| 351 |
3 |
7 |
} else if (!count2) {
|
| 352 |
6 |
8,10 |
while(count1--)
|
| 353 |
4 |
9 |
env->xdf1.rchg[line1++ - 1] = 1;
|
| 354 |
2 |
11 |
return 0;
|
| 355 |
- |
|
}
|
| 356 |
- |
|
|
| 357 |
1 |
12 |
memset(&map, 0, sizeof(map));
|
| 358 |
1 |
12,13 |
if (fill_hashmap(file1, file2, xpp, env, &map,
|
| 359 |
- |
|
line1, count1, line2, count2))
|
| 360 |
##### |
14 |
return -1;
|
| 361 |
- |
|
|
| 362 |
- |
|
/* are there any matching lines at all? */
|
| 363 |
1 |
15 |
if (!map.has_matches) {
|
| 364 |
##### |
16,18 |
while(count1--)
|
| 365 |
##### |
17 |
env->xdf1.rchg[line1++ - 1] = 1;
|
| 366 |
##### |
19,21 |
while(count2--)
|
| 367 |
##### |
20 |
env->xdf2.rchg[line2++ - 1] = 1;
|
| 368 |
##### |
22 |
xdl_free(map.entries);
|
| 369 |
##### |
23 |
return 0;
|
| 370 |
- |
|
}
|
| 371 |
- |
|
|
| 372 |
1 |
24 |
first = find_longest_common_sequence(&map);
|
| 373 |
1 |
25 |
if (first)
|
| 374 |
1 |
26 |
result = walk_common_sequence(&map, first,
|
| 375 |
- |
|
line1, count1, line2, count2);
|
| 376 |
- |
|
else
|
| 377 |
##### |
27 |
result = fall_back_to_classic_diff(&map,
|
| 378 |
- |
|
line1, count1, line2, count2);
|
| 379 |
- |
|
|
| 380 |
1 |
28 |
xdl_free(map.entries);
|
| 381 |
1 |
29 |
return result;
|
| 382 |
|
- |
|
}
|
| 383 |
|
- |
|
|
| 384 |
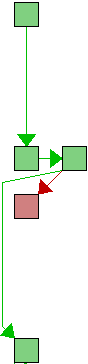 |
1 |
2 |
int xdl_do_patience_diff(mmfile_t *file1, mmfile_t *file2,
|
| 385 |
- |
|
xpparam_t const *xpp, xdfenv_t *env)
|
| 386 |
- |
|
{
|
| 387 |
1 |
2,3 |
if (xdl_prepare_env(file1, file2, xpp, env) < 0)
|
| 388 |
##### |
4 |
return -1;
|
| 389 |
- |
|
|
| 390 |
- |
|
/* environment is cleaned up in xdl_diff() */
|
| 391 |
1 |
5,5 |
return patience_diff(file1, file2, xpp, env,
|
| 392 |
|
1 |
5,5 |
1, env->xdf1.nrec, 1, env->xdf2.nrec);
|
| 393 |
|
- |
|
}
|



